VMware vCenter Server
VMware vCenter Server provides a single point of control of the datacenter. It provides essential datacenter services such as access control, performance monitoring, and configuration.
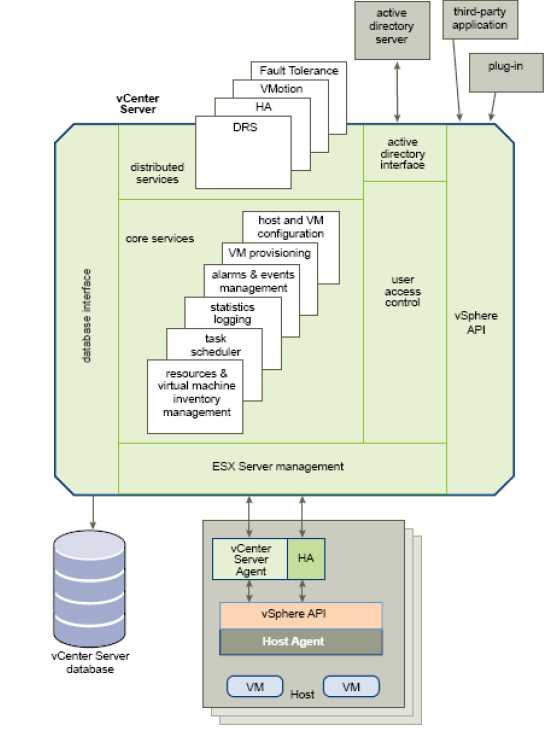
vCenter Server aggregates physical resources from multiple ESX/ESXi hosts and presents a central collection of simple and flexible resources for the system administrator to provision to virtual machines in the virtual environment. vCenter Server components are user access control, core services, distributed services, plug-ins, and various interfaces.
The User Access Control component allows the system administrator to create and manage different levels of access to vCenter Server for different classes of users.
For example, a user class might manage and configure the physical virtualization server hardware in the datacenter. Another user class might only manage virtual resources within a particular resource pool in the virtual machine cluster.
In addition to vCenter Server configuration and management capabilities-which include features such as virtual machine templates, virtual machine customization, rapid provisioning and deployment of virtual machines, role-based access controls, and finegrained resource allocation controls vCenter Server provides the tools for the more advanced features of VMware VMotion, VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler, VMware High Availability, and VMware Fault Tolerance.
In addition to VMware VMotion, VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler, VMware High Availability, and VMware Fault Tolerance, using vCenter Server to manage ESX/ESXi hosts also enables a number of other features:
Enhanced VMotion Compatibility (EVC), which leverages hardware functionality from Intel and AMD to enable greater CPU compatibility between servers grouped into VMware DRS clusters
Host profiles, which allow administrators to bring greater consistency to host configurations across larger environments and to identify missing or incorrect configurations
vNetwork Distributed Switches, which provide the foundation for cluster-wide networking settings and third-party virtual switches
vCenter Server plays a central role in any sizable VMware vSphere implementation. Because of vCenter Server's central role, I'll touch on aspects of vCenter Server's functionality throughout the book. vCenter Server is available in three editions:
vCenter Server Essentials is integrated into the vSphere Essentials edition for small office deployment.
vCenter Server Standard provides all the functionality of vCenter Server, including provisioning, management, monitoring, and automation.
vCenter Server Foundation is like vCenter Server Standard but is limited to managing three ESX/ESXi hosts.
vCenter Server Plug-Ins
Plug-ins are applications that can be installed on top of vCenter Server and that add additional features and functionality. vCenter Server Plug-ins include:
VMware vCenter Converter - Enables users to convert physical machines, and virtual machines in a variety of formats, to ESX/ESXi virtual machines. Converted systems can be imported into any location in the vCenter Server inventory.
VMware Update Manager - Enables security administrators to enforce security standards across ESX/ESXi hosts and managed virtual machines. This plug-in provides the ability to create user-defined security baselines that represent a set of security standards. Security administrators can compare hosts and virtual machines against these baselines to identify and remediate virtual machines that are not in compliance.
vCenter Server Interfaces
vCenter Server interfaces integrate vCenter Server with third party products and applications. vCenter Server has four key interfaces:
ESX management Interfaces with the vCenter Server agent to manage each physical server in the datacenter.
VMware vSphere API Interfaces with VMware management clients and third-party solutions.
Database interface Connects to Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, or IBM DB2 to store information, such as virtual machine configurations, host configurations, resources and virtual machine inventory, performance statistics, events, alarms, user permissions, and roles.
Active Directory interface Connects to Active Directory to obtain user access control information.
