46 What are the various tunneling and encryption protocols SSL VPN
It provides remote access solutions. They are used mainly to provide secure access to the web based applications. As the SSL uses web browser so there is no need to install any additional software for the working of SSL. It operates at the session layer of the OSI model. Applications such as Telnet, FTP, SMTP, IP telephony etc. do not work with SSL because these applications do not use web browsers as their front end interfaces.
There are three general types of SSL client implementations:
1) Clientless
2) Thin Client
3) Network Client
Clientless: When only the web browser is used for SSL VPN they are called as clientless VPNs
Thin client: When Java or Active X software is loaded into the web browser. This added software provides capability to use some non web based applications to be transported across the SSL VPN.
Network Client: In this case the SSL client is required to be installed on the user's desktop. When the user makes a SSL VPN connection to the central site the SSL client is installed on the user's system. User must have required permissions to install SSL client on the system.
SSL VPNs do not provide Layer 3 security to data but in case of clientless VPNs layer 5 protection is provided. SSL VPNs do not provide security to the user data; instead they provide security to the users access to various services and applications on the network. SSL VPNs also provide authentication and access control features. SSL VPNs supports two types of authentication
1) Digital certificates
2) Username and Passwords
VPN
VPN is a virtual connection between the two sites. Suppose there are three sites and for each site to have full meshed connectivity it would require two connections to other two sites as in figure 1.1. This is not a scalable or cost effective solution because if number of sites increase we need dedicated lease lines for each site.
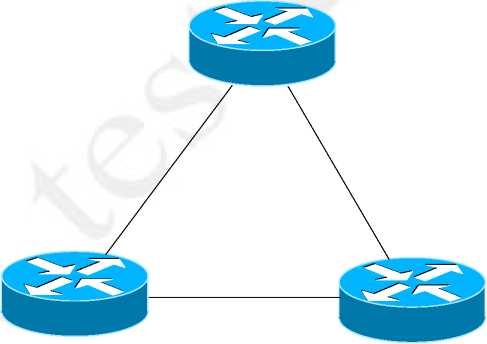
Figure 75: Three Sites connected with leased lines
In order to provide a cost effective and scalable solution VPNs are used. VPN use the share infrastructure of the service provider network hence n number of sites can be connected via virtual circuits for example in fig 1.2
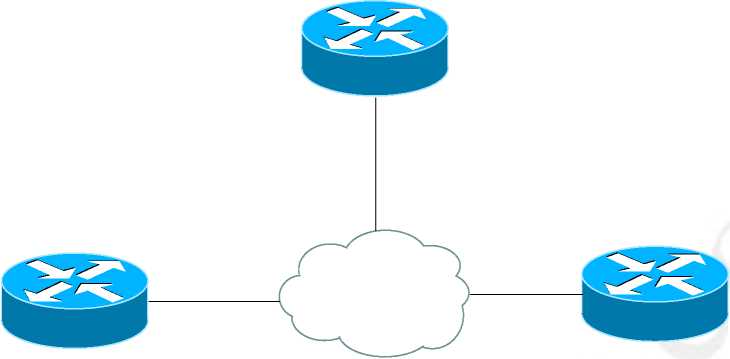
Figure 76: Sites connected via virtual circuits
VPN is an encrypted tunnel that runs from host to host over the service provider's network. It uses various protocols such as IPsec, GRE, SSL etc to provide security services. VPN encrypts the data to protect it from the network attacks and hackers. There are two types of modes that the VPN supports:
1) Tunnel Mode
2) Transport Mode
Tunnel mode: In tunnel mode the source and destination devices do not protect the data. Some other device provides the security to the data. The devices that provide the security on behalf of other devices are called as VPN gateways.
Transport Mode: This type of VPN occurs in between the real source and destination addresses.
There are various types of VPNs such as:
1) Site-to-Site VPNs
2) Remote Access VPNs
3) Firewall VPNs
4) User-to-User VPNs
Site-to-Site VPNs: It uses tunnel mode between the VPN gateways to protect traffic between two or more sites. They are also called as LAN-to-LAN connections (L2L). In case of L2L VPN a central device provides the protection to the user data.
Remote Access VPNs: They are used when the speed of internet connection is very slow between two sites who want to connect to each other via VPN.
Firewall VPNs: It can be a L2L or Remote Access VPN that is provided with an additional security and firewall features. Firewall VPNs are used in case of high security requirement between VPNs.
User-to-User VPNs: It uses a transport mode VPN connection between two devices.
L2TP
L2TP encapsulates the data in PPP frames and then transmits these frames across the IP network. It uses UDP as the encapsulation mechanism for tunnel maintenance and user data. L2TP is a combination of PPTP and L2F. It is defined in RFC 2261 and 3438. L2TP has the best of both protocols PPTP and L2F and combines their advantages into one protocol. It extends the PPP protocol. L2TP requires the services of other protocol to provide encryption. L2TP uses the services of IPsec to provide encryption.
L2TP is a remote access solution which uses client and server architecture. L2TP can use various protocols such as PAP, CHAP and MS-CHAP to provide security features. Working of L2TP
To set up a L2TP tunnel two steps are used:
1) Establish control connection for the tunnel.
2) Establish session to transmit user data across the network.
L2TP uses two kinds of tunnel types:
1) Voluntary
2) Compulsory
Voluntary: In this case host and the server are the end point of the tunnel.
Compulsory: In this case PC is not the end point of the tunnel instead a device that is in front of the PC such as access server acts as the tunnel endpoint.
PPTP
PPTP was invented by Microsoft to provide secure remote access solution. Suppose the traffic flows from the client across the unsecure network to the VPN gateway we need to use PPTP. PPTP is an extension of PPP as PPTP uses PPP it also has PPP features. PPTP can authenticate various network devices with the help of protocols such as PAP, CHAP etc.
PPTP contains several features such as:
1) Compression
2) Encryption
3) User Authentication
4) Data Delivery
5) Client Addressing
- Compression: Compression of data is handled by Microsoft's Point-to-Point Compression (MPPC) protocol within the PPP payload. This is supported by both PPTP and L2TPand normally enabled for dialup clients o Encryption: Encryption of data is handled by Microsoft's Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) protocol within the PPP payload. The encryption uses RSA's RC4 encryption algorithm. PPTP uses this method, whereas L2TP uses IPsec, which is more secure. With MPPE, the initial key created during user
authentication is used for the encryption algorithm and is regenerated periodically.
- User authentication: It is achieved using PPP's authentication methods, such as PAP or CHAP, and others, such as EAP. MPPE support requires the use of MS-CHAPv1 or v2. If you use EAP, you can choose from a wide range of authentication methods, including static passwords and one-time passwords (through the use of token cards).
- Data delivery: Data is packetized using PPP, which is then encapsulated in a PPTP/ L2TP packet. By using PPP, PPTP can support multiple transport protocols, such as IP, IPX, NetBEUI, and others.
- Client addressing PPTP and L2TP support dynamic addressing of the client using PPP's Network Control Protocol (NCP). As mentioned in the last chapter, the Cisco IKE Mode config supports a similar function.
IPSEC
IPsec provides security at the network layer. With the help of IPsec IP traffic can be protected between the two devices. To use IPsec on the client side we need to install additional software to provide layer 3 security. IPsec's is defined in RFC 2401.
The various services provided by the IPsec are:
1) Data confidentiality
2) Data integration and authentication
3) Anti-replay detection
4) Peer authentication
Data confidentiality: It is done with the help of encryption to prevent data theft by various attacks such as eavesdropping. IPsec supports various encryption algorithms such as DES, 3DES and AES.
Data integration and authentication: It is done by using HMAC functions. HMAC verifies that the data packets have not been tampered and are received from an authentic host. MD5 and SHA-1 are supported HMAC functions.
Anti-replay detection: All data packets in IPsec are provided with encrypted sequence numbers to ensure that the replay attack does not take place.
Peer Authentication: It is done to ensure the integrity and authenticity of the peers before they send data.
The two main grouping standards IPsec uses are:
1) ISAKMP/IKE/Oakley/SKEME: These standards are used for setting up a secure management connection.
2) AH and ESP: These standards provide various services like data integrity, data origin authentication and anti-replay etc.
