54 Identify common security threats and mitigation techniques
The various kind of security threats are:
Denial-of-service (DOS) attacks
The main purpose of these attacks is to disable and corrupt the network services. This attack crashes the system or makes it too slow to be working efficiently. DOS attacks are very easy to perform and the main target of these attacks is the web servers. The primary purpose of these attacks is to deny access to the device or network by continuously bombarding the network with useless traffic. The DOS attack is started by the attacker by deploying Zombie programs in various computers that have a very high bandwidth. This type of attack is controlled by the Zombie Master who send information to various compromised Zombie computers. In turn after receiving the information from the Zombie Master the various computers start sending malicious traffic to the target.
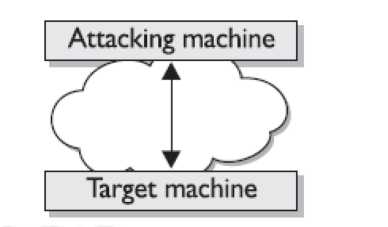
Figure 90: DOS attack with a single attacker and a single target
The new DOS attack is the DRDOS which uses various users to send the TCP SYN request or ICMP ping messages to various hosts using a spoofed source address. Hosts replies to these messages with an unsupportable flood of packets aimed at the target.
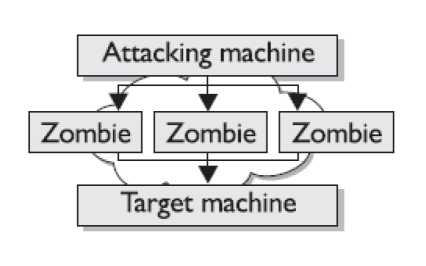
Figure 91: Zombie Attack
Other well known DOS attacks are:
TCP SYN flood, Ping of Death, Trinoo, Tribe Flood Network (TFN) and Tribe Flood Network 2000 (TFN2K), Stacheldraht and Trinity.
Viruses
It is a computer code that attaches itself to the other software running on the computer. Thus each time the software opens the virus reproduces itself and keeps on growing. It can crash the computer system or make it too slow to be operated efficiently. Virus requires some human intervention to spread. An Antivirus software is used to keep the system virus free.
Worm
It is a computer program that exploits the vulnerabilities on the computer or network systems to replicate itself. A worm spreads itself by creating duplicates of itself on the system or network. A worm attached to an email can send copies of email to various addresses in the email system's address books. Examples of worms are Code Red and Nimda.
Attackers
Attackers can be the devices or humans whose purpose is to harm the network or the systems. Attackers attack the network using various techniques such as packet sniffers, port scanners etc. Their main motive is to gain information of the user data or network and destroy files. Some attackers only attack to make the servers or network slow by depleting the servers of their memory. These kind of attacks are called as DOS attacks.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack
It can be thought of a computer between you and the network. It is placed in between to monitor the data you send or receive. In case of man-in-middle attacks the attacker has access to all data that is sent and received from your side. Possible cases are that the middle man can be from the internal of the network or from the ISP end. Man-in-the-middle attacks are usually implemented by using network packet sniffers, routing protocols, or Transport-layer protocols.
The middleman attacker's goal is any or all of the following:
- Theft of information
- Hijacking of an ongoing session to gain access to your internal network resources
- Traffic analysis to derive information about your network and its users
- Denial of service
- Corruption of transmitted data
- Introduction of new information into network sessions
Smurf Attacks
This kind of attack sends large amount of ICMP (internet control message protocol) echo ping to the ip broadcast address from a valid host. This valid host is traceable and is falsely framed as an attacker. These attacks send Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) broadcasts. As the hosts on the network reply to the icmp echo request with an icmp echo reply the bandwidth is consumed in high amounts resulting in denial of service request to the valid users on the network. For example a smurf attack such as fraggle uses the UDP echo packets in same manner as the icmp echo packets. Fraggle is a simple rewrite of smurf to use a Layer 4 broadcast (Transport Layer). To prevent the smurf attacks the networks should perform filtering either at the end of start of network where customers connect or at the start of network where it connects to the upstream routers. The main goal is to prevent the spoofed source addresses from entering or leaving the network.
Rogue Access Points
It is an unauthorized wireless access point (WAP) installed in the network. Rogue access points pose security threats in the network. Suppose a user in your network installs their own wireless networks and they do not know what dangers they are posing for the networks. If a user has some knowledge and installs wireless networks and turns the SSID broadcasting off. The solution of this problem is to run sniffers that detect wireless.
Phishing
It is a method in which the attacker gives an impression as a trusted source or site and requests your personal information. For example an attacker makes a duplicate site as that of your bank credit card and demands your credit card information which he uses for online purchases etc. The user thinks that the information he/she is providing to the original company but is cheated.
