11 Identify the functions of specialized network devices (Multilayer switch, Content switch IDS/IPS, Load balancer, Multifunction network devices, DNS server, Bandwidth shaper, Proxy server, CSU/DSU)
A network is comprised of certain common and specialized network devices. DHCP servers, firewalls are devices that can be found in most network devices and they fall in the category of common devices. There are some devices which are not found in all the networks, these networks are termed as specialized devices. Examples of these devices are load balancers and proxy servers. Discussing some of these devices in detail:
Multilayer Switches: With time the functions of hubs, routers and bridges began to be combined into a single device and the same happened with multilayer switches also. A multi layer switch is one that operates at both layers, that is, layer 2 and 3 of the OSI Model. It can act both as a switch as well as a router. It is a high performance device supporting the same routing protocols as the router and just like a switch it directs the traffic within the LAN and in addition forwards the traffic in the subnets also.
Content Switches: A content switch is a costly device and hence is not used very often. The functions that it performs are receiving data, examining the data, deciding where to send it and forwarding the same. It is able to identify the application for which the data is targeted and forward the same. In addition, content servers help with load balancing as the requests are distributed across the server and target the data for designated servers.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: IDS and IPS are designed in a way that they identify unwanted access and traffic. Both the systems work in manner different from each other.
- IDS: It can be either hardware or software. It constantly monitors both inbound as well as outbound traffic. It has built in parameters that flag and document traffic that may be doubtful. It stops after detecting the threat and issuing an alarm. Further action is left for the administrator to take. The inbound and the outbound traffic is compared to a large database containing attack signatures. Attack signatures are features of attacks that were identified at other places. IDS can identify such attacks. In other words IDS maintains an updated database of such attacks.
ID systems can be host based or network based. It cannot be used as an alternative to firewall as both have different functions to perform. A firewall prevents unwanted traffic from entering the system, whereas, an IDS detects the intrusion after it has been made, that is, even after it has managed to pass firewall.
- IPS: An Intrusion Prevention System is more hands on. It tries to manage the attacks on its own. In addition to the function of monitoring and flagging an IPS takes immediate action to deal with such threats. An IDS only flags the threats whereas an IPS immediately tries to shut the intruders out.
Load Balancer: Network servers do all the main function in a network. They hold data, distribute data, maintain data back ups, and take care of security of the network. There is too much to do for a single server. A load balancer steps in at this point. Load balancing is the technique of distributing the workload amongst several servers. This goes a long way in increasing the performance, reliability and availability of the network.
Multifunction Network Devices: These devices combine the function of individual devices like the hubs, routers, DHCP server, wireless access point and repeaters in one. They offer many advantages over independent devices. An organization maintaining antivirus, firewall, filtering and other such facilities has to pay for all these along with the staff that is required to maintain all these. It is better to replace all these with one single multifunction network device.
DNS Server: The full form of the acronym DNS is Doman Name System. It performs a very basic but a very important function. The function that it performs is of name resolution from hostnames to IP addresses. The function to be performed is simple but not the procedure undertaken. A DNS server consults the database that it maintains, and the other DNS servers for the required information. The process is a culmination of multiple queries. DNS permits the use of easy to remember hostnames. It assists in finding the correct the hostname. Once the correct TCP/IP address is ascertained it is sent back to the client. The address is added to the cache and for subsequent contacts, direct access is made. Most of the operating systems have the ability to act as a DNS server. The degree of sophistication may vary but essentially the process remains the same. The quantum of power that a DNS server requires is proportional to the requests that it handles.
Bandwidth Shaper: The presence of internet and intranet facilities on a network requires a high amount of bandwidth. It comes under the purview of the administrators to ensure that the demand of bandwidth is fulfilled and adequate resources be distributed for important functions over spam or peer to peer downloads. Network traffic needs to be monitored for this. Bandwidth shaping is the technique that id used to control the use of bandwidth on the network. It attaches a priority value with every set of data traveling to and fro the network. It essentially does the functions of:
- Monitoring: This helps to identify the places and the times of the day when bandwidth usage is high;
- Shaping: Customizing the availability of bandwidth after studying the data that has been received is termed as shaping.
The figure given below illustrates an example of a bandwidth shaper.
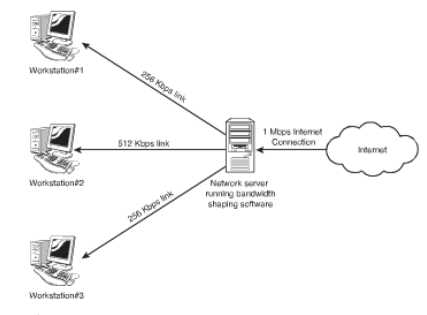
Figure 37: A Bandwidth Shaper
Proxy Server: Proxy servers are considered as an integral part of firewalls. However the role that is performed by proxy servers is very different from that of a firewall. It is a server that sits between a client computer and the Internet. Sitting there its job is to look
for the pages that have requested by the client. It checks the target of the request, that is, whether it is intended for the internet or the local web server. It forwards the request to its intended destination and receives the information back, which it then sends back to the client.
There is no doubt about the fact this slows down the process, but the advantage is the facility of caching that the server provides. Cache is the place where the server makes a copy of the page that was requested from the internet. On a subsequent request for the same page, the request is catered to from the cache rather than going to the internet. This increases the response time and reduces the pressure on bandwidth. The figure given below illustrates the working of a proxy server. The disadvantages of using the cache are:
- It is not displaying the recent page from the internet;
- They are not suitable for blocking numerous websites, though can effectively block a few
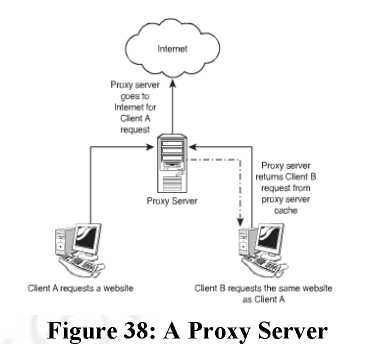
Figure 38
CSUs/DSUs: These do the job of translators between the LAN and WAN data formats. This conversion becomes necessary as the technologies used by both are different. These can also be considered to be a type of digital modem. It changes the signal from one digital format to another digital format. The figure given below illustrates how CSU/DSUs are to be integrated into a network.
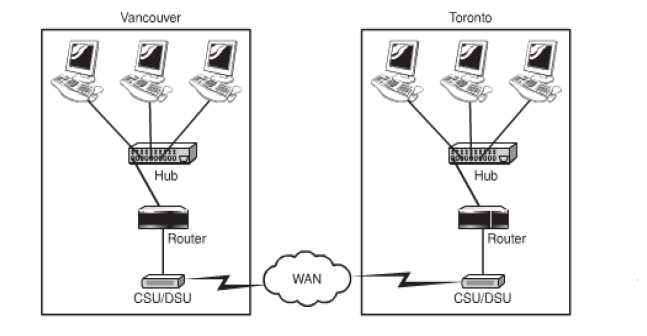
Figure 39: Usage of a CSU/DSU in a Network
